Diesel generators power plant
Explore the advantages of diesel generators in emergency power supply scenarios, highlighting their reliability, efficiency, and long operational life compared to alternative power sources
Diesel power generation plant means where it’s used for mobile, peaking, standby, and backup for self-consumption of main power. mainly used for small power. But it is also being used as a large-scale peaking plant in the modern era. Due to geographical conditions, diesel power generation plant is required in many parts of the world. Like Alaska, These places have no grid transmission lines, Grid companies continue to use diesel generator plants as their component and must control their own voltage and frequency.
Mobile types plant: its used for small users like shops, and houses. They have a unit capacity of 100 KW.
Standby or backup plant: It is mainly used as an alternative to mains power in large factories. It is even sometimes used as a main power. Usually, 300-400 KW capacity is completed. Diesel is used as fuel. Many companies are made this types of generator such as- Caterpillar Inc., Perkins Engines, Cummins etc.
Peaking Plant: It mainly produces electricity on a large scale, which is fed into the national grid of the region. And power grid companies regulate the frequency and voltage of these systems. Generally the production capacity is 50-400 MW. Their generation voltage is 11 KV and step-off is 33 KV, 230 KV transmissions. These plants are large scale and engine based. Various big companies in the world make this type of diesel engine. Such as: Rolls-Royals, Watsila, and MAN etc. Due to more capacity engines, a lot of auxiliary equipment is needed to operate them. Some are engine mountings and some are used as accessories. Detailed discussion about engine based peaking power plant is given below. Three types of fuel are used in peaking plants.
- HFO (heavy fuel oil)
- LFO (light fuel oil or diesel)
- Gasoline (Natural gas)
How to work diesel engine:
Diesel engine also known as internal combustion (IC) engine which works as according to four storks cycle processes. Piston completes the four separate strokes by crank or moves the crankshaft. The strokes are described below:
- Suction strokes: In this stroke, the piston moves to the top dead center (TDC) and ends at the bottom (BDC). In this stroke, the inlet valve opens, causing air to be drawn into the cylinder by creating a reciprocating vacuum.
- Compression stroke: These strokes start just after the suction stroke ends. In this stroke, the piston moves from the bottom dead center to the top dead center. During this time both the inlet and the exhaust valve are closed. Which consequently increases the pressure and temperature of the intake air?
- Power stork: In this stroke, the crankshaft completes half of 360°. At this point(just end of the compression stroke), the piston is at the top dead center (TDC), and this time the high pressure and temperature air is generated and diesel is injected into the air, causing combustion to occur. The generated force pushes the piston towards the bottom dead center, which in turn accelerates the crankshaft rotation.
- Exhaust stork: In this stroke, the piston moves from the bottom dead center (BDC) to the top dead center (TDC). At this time the exhaust valve opens allowing the burnt gas to escape through the exhaust valve.
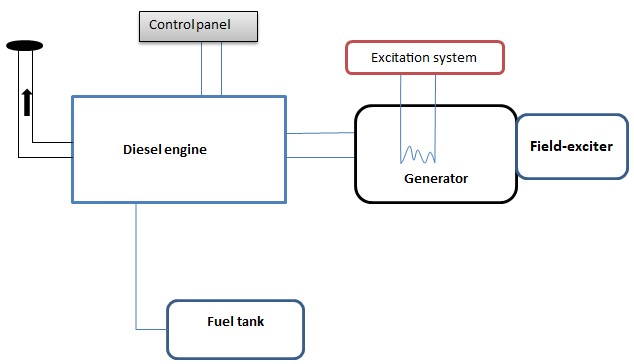
Diesel generator power plant system
Diesel generator power plant is made of various processes and auxiliary systems. In modern science, multiple companies make their machinery and develop efficiency through various factors.
Diesel/HFO or gasoline is a hydrocarbon fuel that is refined from crude oil. Electricity is one of the basic needs of our modern life. Especially residential and commercial sectors can be imagined without electricity. So this power generation requires efficiency and reliability. Reliability is considered a very important factor, especially concerning.
- Plant systems:
- Fuel system
- Cooling water System
- Air System
- Heating System
- Exhaust system
- Lubricating System
- Power system
- Charge air system
- Electric system/Generator
Fuel system: Diesel generator power plant mainly uses three types of fuel. Such as Diesel oil (LFO) and heavy fuel oil (HFO) and natural gas. HFO and natural gas are used for all time generation, on the other hand, diesel use only starts and stops before major maintenance or long time stop. Although diesel is now used as the main fuel in many picking plants.
Cooling system: The engine has two cooling water systems. The high-temperature freshwater system cooling the engine (Jacket water), the turbocharger, and possibly the first stage is the charge air cooler. The low- low-temperature water system cools the charged air, lube Oil, and High-temperature Freshwater. The low- temperature System is usually a freshwater system, but a seawater system.
High-temperature freshwater system (jacket water system):
The high-temperature fresh water is circulated by an electrically driven or engine-driven pump. If the engine has a 2-stage charge air cooler, the cooling water flows through the charge air cooler’s first stage. If it has a one-stage charge air cooler, the cooling water is supplied directly to the distribution pipe. From the distribution pipe, cooling water is supplied to each cylinder liner, and through branch pipes to the turbocharger.
Low-temperature freshwater system:
The Low low-temperature fresh water is circulated by an electrically driven or engine-driven pump – and is normally led in series through the charge air-,lubr. Oil and freshwater coolers. If the engine has a 2-stage charge air cooler, the low-temp. Water is used for cooling the 2nd stage, which is bypassed at low engine load.
Diesel engine air system: Here two types of air are used, one is for the starting system and the other is used for the control system (Pneumatic valve).
When starting the engine, control current is sent to the release valve (9). The release valve opens, and the starting air is led to the starting air valves in the cylinder heads and to the pilot air distributor. Pilot air is led from the distributor to each of the starting air valves which open for the main air to each cylinder.
Generator/Electric system: An A.C. Generator or Alternator is a device that uses mechanical energy to produce alternating or variable electromotive force (emf) or voltage.
Transmission: The transport of electricity from the output of the generator through the transformer to the load center is called transmission.
Factors in Selecting the Site of a Diesel Power Plant

Several factors need to be considered when choosing the location of a diesel power plant:
Distance from Load Center: The plant should be near the load center to minimize transportation costs, maintenance, and power loss.
Water Supply Facility: Adequate water supply is crucial for cooling the diesel engine.
Strong Foundations: Since diesel power plants generate significant vibration, the foundation must be solid, and the soil should be strong enough to support it.
Communication: The site should have easy access for fuel delivery, parts supply, and personnel involved in the project.
Local Conditions: In areas where sand or debris is present, air, lube oil, and fuel filters can become costly. If not properly filtered, these particles can reduce the life of the engine and prime mover.
Pollution: The location should ensure that surrounding residents are not disturbed by smoke, noise, or other emissions from the diesel plant.
Market Facilities: The plant should be located near a market where essential parts like fuel, lubricating oil, and daily necessities for the plant’s employees can be easily procured.
Future Expansion: The selected site should allow space for future expansion, enabling the installation of new units to increase the plant’s capacity.
Application of a Diesel generator Power Plant
- Diesel power plants are useful for generating mobile power, such as for roads, railways, and rivers.
- They act as base plants for producing electricity.
- They function as standby power centers.
- They serve as peak load plants for special types of power plants.
- In remote areas where setting up substations is impossible and power demand is low, they are used as nursery stations.
- Diesel plants are profitable in industries with low power demand.
- These plants are used to operate auxiliary equipment before starting the main power plant.
- They act as small plants to meet power demand during sudden power outages.
Advantages and disadvantages of diesel generator power plant
Advantages:
Diesel plant layout, design, and construction are simple.
It requires less time to start and accept load without any delay.
It takes less space and building requirements.
Low initial cost.
Able to supply power according to partial demand.
Fewer people are needed to run the center.
Fuel transportation, supply, and related problems are less.
Water supply requirements are low.
Requires less time to deploy.
It has high efficiency.
Placing it very close to the supply center is advantageous.
Disadvantages:
Diesel fuel is expensive compared to other fuels.
It is not capable of running on overload for long periods.
Lubrication cost is high.
It cannot be used for higher power demands.

